|
| Fig.1. Gas analysis device for malfunction diagnosis of high voltage transfomers |
At present, the analysis is performed using the flame-ionization (FI) and the thermal conductivity (TC) detectors. Such scheme of analysis is bulky, inconvenient and expensive, because needs a lot of rare gas (Ar and He).
When compared to other analytical systems, the proposed device provides a simpler (fewer samples required), low cost (no inert gases), and more accurate way to diagnose transformer malfunctions.
The device allows analysing all of the gases dissolved in the transformer oil. The main part of the device is an adsorption semiconductor sensor based on metal oxides as sensing element of adsorption-semiconductor detector (ASD). Combination of ASD and preliminary chromatographic separating of analysed sample provides selective gas measuring. Moreover, high sensitivity of the sensor to organic and inorganic gases allows realising new chromatographic analysis scheme of gases dissolved in the transformer oil.
The device include two blocks: detector block (ASD), which has an autonomous supplying, and electronic block of measuring and regulating the operation of ASD (Fig.1)
| Fig.2. The gas analysis device in combination with chromatogrph GC - 14B |
- fast acting adsorption-semiconductor sensor with a high sensitivity to micro-concentrations of H2, CH4,C2H6, C2H4, C2H2 and ÑÎ in air.
- design and electrical circuit of the AS detector which provide optimal conditions of the sensor action in the chromatographic mode.
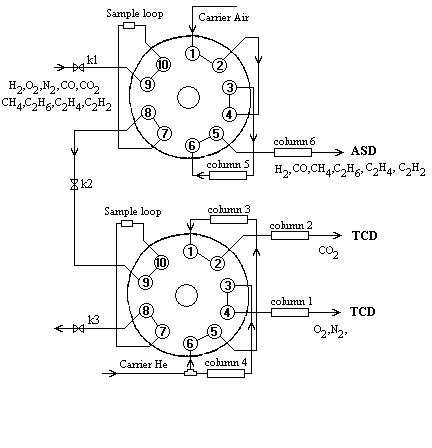
The developed device can work in a combination with any chromatograph, which has the thermoconductometric detector (TCD) (Fig.2). The scheme of measurement of all gases, which dissolved in the transformer oil, using TCD and ASD is shown on Fig 3.
Application of the device will promote energy saving and omitting emergency situations in power systems.
Development of the device was carried out in the course of the STCU project 1589
|
| Fig. 3. The scheme of measurement of all gases, which dissolved in the transformer oil |
